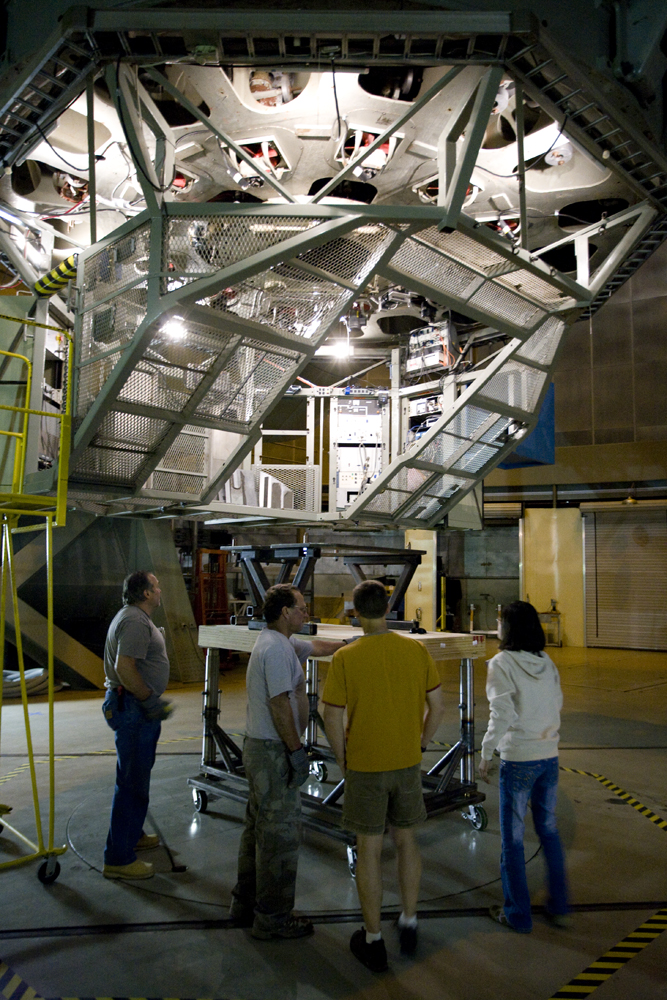
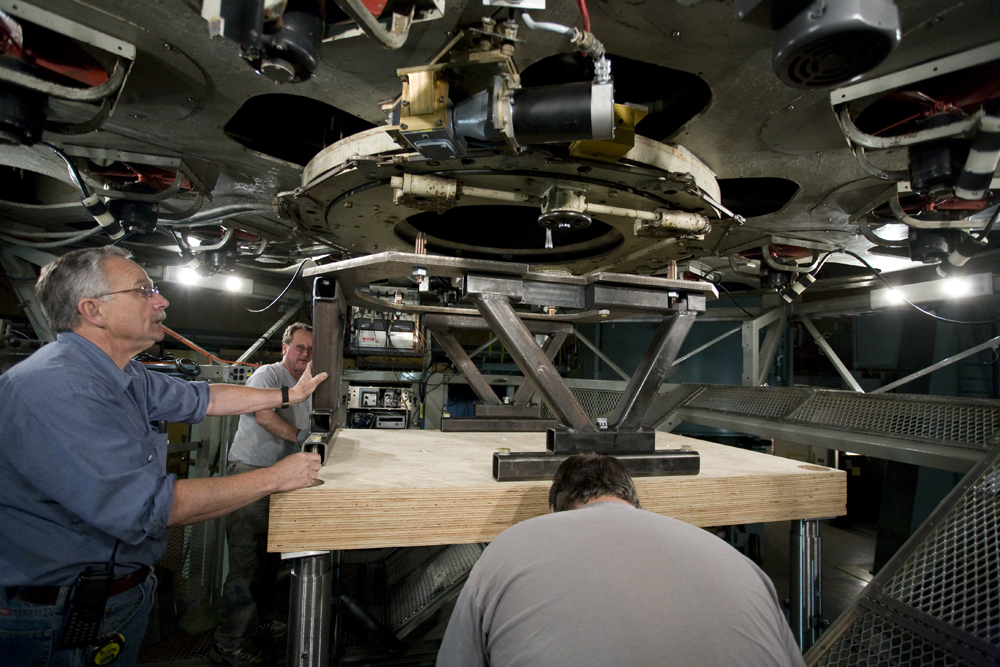
I thought that the readers of Palomar Skies might like summary of the projects coming our way this fall, so here goes.

Photo by Iair Arcavi.
Transients are all the rage and 13 nights, spread out across the months, will be devoted to following up on objects discovered with the Palomar Transient Factory survey. An additional four nights will be devoted to doing similar work, but for transients discovered via the Catalina Real-Time Transient Survey. Both of these programs will primarily use our visible light spectrograph to identify the type of transients discovered. One other night will specifically devoted to a particular type of supernova known as a Type Ia.
The other big item on the agenda for 2011B is the study of exoplanets. Some of this is follow-up work from the Kepler mission. 14 nights are devoted to various studies on Kepler exoplanets or their host stars. Much of this is visible or near infrared spectroscopy, but some of it also makes use of our newly souped-up adaptive optics system known as PALM-3000. This high-resolution imaging system will be used 12 nights to study and hunt for exoplanets and planet-forming disks of debris located around young stars. Using instruments other than the AO system, two nights will be used to study some of these disks discovered by the WISE mission and another two to study some “hot Jupiters” as they are seen to transit their host stars. All together that comes to 30 nights of exoplanets in 2011B or 1/6th of the telescope time.
Speaking of planets and things that orbit a star, worlds of our own solar system are a subject of study too. This includes studies of asteroids (8 nights), the Galilean moons of Jupiter (1), the irregular satellites of the outer planets (2), the atmosphere of Uranus (1), and the frozen world located beyond Neptune in the Kuiper Belt (2).
Looking a little further out, 12 nights will be devoted to studying brown dwarfs, so called “failed stars” – objects that are more massive than a planet but not massive enough to sustain nuclear fusion the way that stars do. Many of the objects to be observed were first discovered by the WISE mission.
Lots of stellar astrophysics will be going on as our astronomers study star formation (3), young stars and protostars (4), young variable stars, novae (4), white dwarfs (2), x-ray binary systems (1). The presence of dark matter in our own galaxy will be mapped via studies of the motions of RR Lyrae type variable stars that are part of the Pisces tidal stream (3).

Photo by Iair Arcavi.
Looking beyond our galaxy is still a big part of science at Palomar. In fact, aside from engineering time, it comprises the rest of the time on the schedule. Massive stars and the chemistry of the stars in M31 (aka the Andromeda Galaxy), our nearest big galaxy, will be the subject of study for 8 nights. Included on the list are blue compact dwarf galaxies (2), massive elliptical galaxies (5), hyperluminous galaxies (1), low-luminosity star-forming galaxies (5), galaxies known as Lyman-alpha emitters (7), luminous infrared galaxies (7), and galaxy clusters (6). Five nights will be directed toward the evolution of galaxies and six nights will be devoted toward using the Cosmic Web Imager instrument to map out the presence of gas located between galaxies.
Supermassive black holes, which lie at the core of quasars and various galaxies with active galactic nuclei are to be studied for six nights, while quasars themselves are studied another seven nights. The environment in and around another type of active galaxy – radio galaxies— is to be studied for five nights.
It takes time to keep the telescope & its instrumentation in tip-top shape. Seven nights will be lost because we will be re-aluminizing the 200-inch mirror in October. An additional twelve nights will be spent on engineering various scientific cameras, mostly related to our new PALM-3000 adaptive optics system. Two of those nights will be a demonstration of a new instrument known as ARCONS – the ARray Camera for Optical to Near-IR Spectrophotometry. It is likely that there will be science observations on a good fraction of these “engineering” nights.
Finally, we will be closed to astronomy and engineering December 24 & 25 for our only two holidays of the year.
There is the summary of what we will be looking at from August through January. Hopefully I didn't miss anything.